Special IP addresses in GNS3
GNS3 uses several RFC1918 private IP ranges by default. If possible we recommend to avoid using them in your topology in order to limit conflicts.
IP Reserved by GNS3
NAT: 192.168.122.0/24
Starting with GNS3 2.0 this IP range is used by the NAT node (powered by libvirt).
It runs a DHCP server and DNS relay on its internal “nat0” interface, which is assigned 192.168.122.1. Topology devices are able to use this node, both for automatic addressing, as well as to easily allow them to access the internet with minimal set up work.
(you’ll see this IP assigned to virbr0 in the GNS3 VM’s bash shell)
VPN: 172.16.253.0/24
This range is used only when you connect to a GNS3 remote server via VPN. These IPs are not visible in GNS3 until you use the Cloud Object to connect your real network to your GNS3 topology.
IP Reserved by Emulators
This IPs are not visible in GNS3 until you use the Cloud object to connect your local LAN to your topology.
IP reserved by Docker
If docker is installed, be careful to this IP range:
DOCKER0: 172.17.0.0/16 This the default range use by docker0
IP reserved by VMware
VMWARE VMNET: 192.168.0.0/16 For each vmnet created in VMware (either directly via its Virtual Network Editor), or by using the gns3vmnet executable, it will have a random 192.168.x.x/24 subnet address and a DHCP server automatically created.
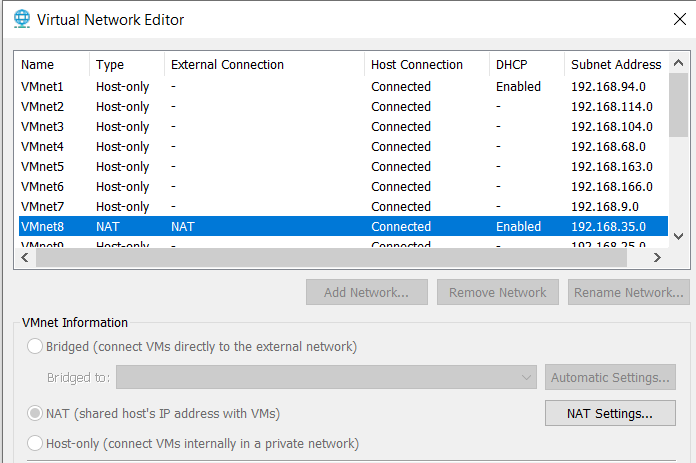
This is an example of the subnet addresses VMware automatically created for each of new host-only vmnets. When adding a VMware VM into a GNS3 topology, it must be a host-only vmnet with the DHCP server turned off.
More information about using VMware VMs in GNS3 topologies can be found in this article.