Cisco IOS images for Dynamips
GNS3 offers multiple ways to emulate IOS. For older images, we use and maintain Dynamips; an emulator dedicated to emulate some Cisco hardware. Dynamips can run unmodified IOS images. In the new GNS3 1.4, there is a way to run a second category of switches and routers. These are classified as Routing and Switching virtual machines (or R+Svms) for short. What are the differences? Here are the major differences:
- IOS images are usually run in Dynamips however R+Svms are housed in a virtual machine.
- IOS images are lower in cpu and memory so you can fit more of them in one topology.
- R+Svms are all vendor Routing and Switching images that are larger in size but can be imported into GNS3 for real world network emulation.
Important Points
Availability
Due to these platforms hitting End of Sale, End of Life, and End of Support status, the images are no longer available for download from Cisco’s support sections. Currently, the c7200 images are the only ones still available for download for those with a support contract.
IOS 15.x
Only the c7200 series get newer IOS 15 images. All other platforms are now end-of-life and only support IOS 12.4. Please note that the IOSv appliance is based on IOS 15 and there are IOU (IOS on UNIX) images with IOS 15.
Should I use a mainline and technology train image?
You will find the technology train images to contain the newest features but it may also contain the most bugs. We recommend Mainline over Technology train if you are interested on stability without the need of new features.Please see Cisco IOS Versions and Naming for more information.
Minimum memory
The minimum RAM is the amount of memory needed for IOS to work at maximum capacity with most feature configured and activated. From experience you can usually use a bit less RAM just fine.
Recommended images
We really recommend using the c3640, c3660, c3725, c3745 and c7200 IOS images listed below, they have proven to be the most stable in GNS3 provided you use the right amount of RAM and Idle-PC value.
Idle-PC value
When Dynamips runs an IOS image, a single instance can consume 100% of the processing time for a CPU core or thread. To remedy this, you can supply Dynamips with an Idle-PC value, to consume less CPU. This value will vary between devices/images. To help automate the process of determining a valid Idle-PC value, you can use the Idle-PC finder button when importing a supported IOS image into GNS3:
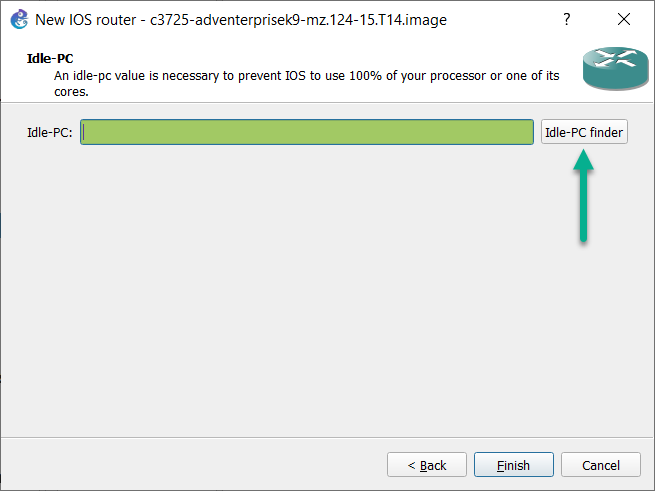
(Idle-PC values are not required with virtual machines or docker containers. They’re only required for use by the Dynamips emulator)
C1700 Series
1700s have 1 FastEthernet fixed port (C1700-MB-1ETH) on its motherboard, 2 subslots for WICs (maximum of 2 Ethernet ports or 4 serial ports), and no Network Module slots. Note that interfaces do not use a slot designation (e.g. “f0”)
IOS version 12.4.25d (Mainline)
File name: c1700-adventerprisek9-mz.124-25d.bin MD5: 3ed8d56a8757771105a56070e4147716 Minimum RAM: 128MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x80358a60
IOS version 12.4.15T14 (Technology train) File name: c1700-adventerprisek9-mz.124-15.T14.bin MD5: 351190de8764263e85a2b50718f394fd Minimum RAM: 160MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x824a4dc4
C2600 Series
2600s have one or two Ethernet or FastEthernet interfaces on its motherboard, 3 subslots for WICs (maximum of 6 serial ports) and 1 Network Module slot (maximum of 4 Ethernet ports or 16 FastEthernet ports).
IOS version 12.4.25d (Mainline)
File name: c2600-adventerprisek9-mz.124-25d.bin MD5: 8eca1f6fe57dfb3c3cf3568c0e475853 Minimum RAM: 128MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x80519c48
IOS version 12.4.15T14 (Technology train)
File name: c2600-adventerprisek9-mz.124-15.T14.bin MD5: 12b8548b23e2ec593652ae9310ac797f Minimum RAM: 256MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x8027ec88
C3620
The c3620 supports up to 2 Network Modules (maximum of 8 Ethernet ports, 32 FastEthernet ports or 8 serial ports). Note that tt shouldn’t be used since the latest available IOS image is very old.
IOS version 12.2.26c
File name: c3620-a3jk8s-mz.122-26c.bin MD5: dd34b958ad362ef54ba48b187f4c97b4 Minimum RAM: 64MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x603a8bac
C3640
The c3640 supports up to 4 Network Modules (maximum of 16 Ethernet ports, 32 FastEthernet ports or 16 serial ports).
IOS version 12.4.25d (Mainline)
File name: c3640-a3js-mz.124-25d.bin MD5: db9f63ca1b46d18fb835496bfffe608a Minimum RAM: 128MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x6050b114
C3660
The c3660 has 2 FastEthernet fixed ports (Leopard-2FE) and supports up to 6 Network Modules (maximum of 24 Ethernet ports, 32 FastEthernet ports or 24 serial ports).
IOS version 12.4.25d (Mainline)
File name: c3660-a3jk9s-mz.124-25d.bin MD5: 4ac7e947f13c189d746149dc74992890 Minimum RAM: 192MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x606071f8
IOS version 12.4.15T14 (Technology train)
File name: c3660-a3jk9s-mz.124-15.T14.bin MD5: 39950b7a563aa08e94a168260409f1e6 Minimum RAM: 256MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x6076e0b4
C2691
The c2691 has 2 FastEthernet interfaces its motherboard (GT96100-FE), 3 subslots for WICs (maximum of 6 serial ports) and 1 Network Module slot (maximum of 16 FastEthernet ports or 4 serial ports).
IOS version 12.4.25d (Mainline)
File name: c2691-adventerprisek9-mz.124-25d.bin MD5: a8e1f5821d87456595488d6221ce42e5 Minimum RAM: 192MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x60a48cb8
IOS version 12.4.15T14 (Technology train)
File name: c2691-adventerprisek9-mz.124-15.T14.bin MD5: 91388104d7276ad09204e36d2dfcf52d Minimum RAM: 256MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x60bcf9f8
C3725
The c3725 has 2 FastEthernet interfaces on its motherboard (GT96100-FE), 3 subslots for WICs (maximum of 6 serial ports) and 2 Network Module slots (maximum of 32 FastEthernet ports or 8 serial ports).
IOS version 12.4.25d (Mainline)
File name: c3725-adventerprisek9-mz.24-25d.bin MD5: ac3d313d3caff5beeee244b81d2c024c Minimum RAM: 128MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x602467a4
IOS version 12.4.15T14 (Technology train)
File name: c3725-adventerprisek9-mz.124-15.T14.bin MD5: 42baf17af10d9a1471bf542f0bfd07c7 Minimum RAM: 256MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x60c09aa0
C3745
The c3745 has 2 FastEthernet interfaces on its motherboard (GT96100-FE), 3 subslots for WICs (maximum of 6 serial ports) and 4 Network Module slots (maximum of 32 FastEthernet ports or 16 serial ports).
IOS version 12.4.25d (Mainline)
File name: c3745-adventerprisek9-mz.124-25d.bin MD5: 563797308a3036337c3dee9b4ab54649 Minimum RAM: 256MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x60aa1da0
IOS version 12.4.15T14 (Technology train)
File name: c3745-adventerprisek9-mz.124-15.T14.bin MD5: a696619869a972ec3a27742d38031b6a Minimum RAM: 256 RAM Proposed idle-PC value: 0x602701e4
C7200 SERIES
7200s have a different architecture. Only the 7206 is supported, it has 6 Port Adapters (PA) slots. VXR chassis, NPE-400 and C7200-IO-FE are the default settings in GNS3.
IOS 15 (Mainline)
This router series is still getting new IOS 15.x versions. The last one at this date is: File name: c7200-adventerprisek9-mz.152-4.M8.bin Minimum RAM: 512MB
IOS 12.4.25g (Mainline)
MD5: 3a78cb61831b3ef1530f7402f5986556 File name: c7200-a3jk9s-mz.124-25g.bin Minimum RAM: 256MB
IOS 12.4.24T5 (Technology train)
This one is not the latest 12.4 version but it is easier to find. MD5: 3c4148f62acf56602ce3b371ebae60c9 File name: c7200-adventerprisek9-mz.124-24.T5 Minimum RAM: 256MB Proposed idle-PC value: 0x606df838
Cisco Catalyst Switches
Dynamips is incapable of running IOS images from Catalyst Switches, as it’s unable to emulate the ASICs used in those type of devices.
For switching, you can use an IOU L2 binary image, or an IOSvL2 virtual disk image with Qemu.
However, if you want to use Dynamips you can use the EtherSwitch module with 2600s, 3600s and 3700s Series. Keep in mind that this module works differently (it uses the vlan database etc.) and does NOT support the following features:
- Access Switch Device Manager (SDM) Template
- ACL – Improved Merging Algorithm
- ARP Optimization
- BGP Increased Support of Numbered as-path Access Lists to 500
- BGP Restart Neighbor Session After max-prefix Limit Reached
- BGP Route-Map Continue Support for Outbound Policy
- Clear Counters Per Port
- DHCP Snooping
- DHCP Snooping Counters
- Diagnostics Options on bootup
- ErrDisable Reactivation Per Port
- ErrDisable timeout
- EtherChannel – Flexible PAgP
- Etherchannel Guard
- Fallback Bridging
- Flex Link Bi-directional Fast Convergence
- Flex Link VLAN Load-Balancing
- Flex Links Interface Preemption
- GOLD – Generic Online Diagnostics
- IEEE 802.1ab, Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- IEEE 802.1s – Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) Standard Compliance
- IEEE 802.1s VLAN Multiple Spanning Trees
- IEEE 802.1t
- IEEE 802.1W Spanning Tree Rapid Reconfiguration
- IEEE 802.1x – Auth Fail Open
- IEEE 802.1x – Auth Fail VLAN
- IEEE 802.1x – VLAN Assignment
- IEEE 802.1x – Wake on LAN Support
- IEEE 802.1X Multi-Domain Authentication
- IEEE 802.1x RADIUS Accounting
- IEEE 802.1x with Port Security
- IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation (LACP)
- IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet
- IGMP Fast Leave
- IGMP Version 1
- IGRP
- IP Phone Detection Enhancements
- IP Phone Enhancement – PHY Loop Detection
- IPSG (IP Source Guard)
- Jumbo Frames
- L2PT – Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
- MAC Authentication Bypass
- MLD Snooping
- Multicast Etherchannel Load Balancing
- NAC – L2 IEEE 802.1x
- NAC – L2 IP
- NAC – L2 IP with Auth Fail Open
- Packet-Based Storm Control
- Per Port Per VLAN Policing
- Port Security
- Port Security on Private VLAN Ports
- Private VLANs
- QoS Policy Propagation via Border Gateway Protocol (QPPB)
- Rapid-Per-VLAN-Spanning Tree (Rapid-PVST)
- Reduced MAC Address Usage
- Remote SPAN (RSPAN)
- Smart Port
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) – Loop Guard
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) – PortFast BPDU Filtering
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) – Portfast Support for Trunks
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) – Root Guard
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) – Uplink Load Balancing
- SRR (Shaped Round Robin)
- Standby Supervisor Port Usage
- STP Syslog Messages
- Switching Database Manager (SDM)
- Trunk Failover
- Trusted boundary (extended trust for CDP devices)
- Unicast Mac Filtering
- UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- VLAN Access Control List (VACL)
- VLAN Aware Port Security
- Weighted Tail Drop (WTD)
- Routing and Switching Virtual machines from Vendors
To recap: You can import many images using Virtualbox or VMWare. ASIC based models like the Cisco Catalyst switches are impossible to import as a Routing and Switching image.
If you require more switching features, it is recommended to use larger Virtual Machine Switches and Routers (like the ones from VIRL) that run inside your choice of Qemu, Virtualbox or VMWare. For advanced switching IOSv and/or IOU is recommended.